Introduction to Privacy by Design:
Privacy by design is a framework that integrates privacy solutions in the early phases of a project. By implementing this measure any potential privacy threat or vulnerabilities can be identified or rectified before they become larger issues later on. It is a framework through which organizations of all sizes can embed privacy into their systems and technologies.
The framework was developed by Ann Cavoukian, the former Information and Privacy Commissioner of Ontario, Canada, in the 1990s. It has been adopted by various organizations and authorities around the world including the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). This is a proactive and preventive way of ensuring that privacy is respected and protected in the digital age. It can benefit both users and providers by enhancing trust, reputation, and compliance.
Seven Fundamental Privacy by Design Principles:
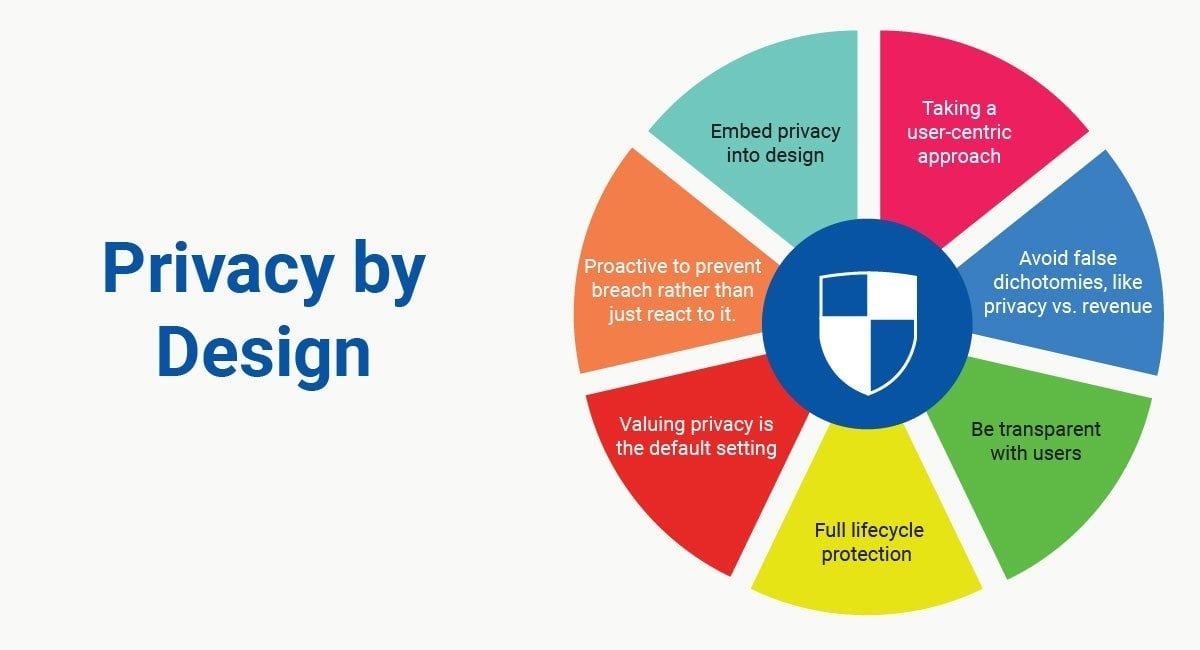
It is an approach to systems engineering that is based on the following seven principles:
-
- Proactive not reactive: The first principle is to be proactive, not reactive. This means that organizations should consider privacy from the outset of the design process, not as an afterthought. This can be done by conducting a privacy impact assessment (PIA) to identify and mitigate privacy risks.
- Privacy as the default setting: The second principle is to make privacy the default setting. This means that privacy should be built into the design of systems and technologies, not something that users have to opt into. This can be done by using privacy-preserving technologies such as encryption and pseudonymization.
- Privacy embedded into design: The third principle of Privacy by design is to embed privacy into the design of systems and technologies. This means that privacy should be considered at every stage of the design process, from requirements gathering to implementation. This can be done by involving privacy experts in the design process and by using privacy-by-design tools and frameworks.
- Full functionality – positive-sum, not zero-sum: The fourth principle is to achieve full functionality while protecting privacy. This means that organizations should not see privacy and functionality as mutually exclusive. It is possible to have both. This can be done by using privacy-preserving technologies and by designing systems and technologies that are flexible and adaptable.
- End-to-end security – lifecycle protection: The fifth principle of Privacy by design is to protect privacy throughout the lifecycle of a system or technology. This means that privacy should be protected from collection to use to disposal. This can be done by using security measures, such as encryption and access controls, throughout the lifecycle of a system or technology.
- Visibility and transparency: The sixth principle is to give individuals visibility and transparency into how their personal information is being collected, used, and shared. This means that organizations should provide clear and concise information about their privacy practices. This can be done by creating privacy policies and procedures that are easy to understand and by providing users with access to their personal information.
- Respect for user privacy: The seventh principle is to respect user privacy. This means that organizations should give users control over their personal information and should allow them to exercise their privacy rights. This can be done by providing users with the ability to opt out of data collection and sharing, and by allowing them to access and correct their personal information.
Benefit from the Privacy by Design Approach:
There are many benefits to using the privacy framework, including, including:
- Increased trust: Users are more likely to trust organizations that adopt principles related to privacy. When organizations are seen as being committed to protecting privacy, they are more likely to win the trust of their customers and stakeholders. This can lead to increased customer loyalty and sales.
- Reduced risk of data breaches: It can help organizations to reduce the risk of data breaches, which can save them money and protect their reputation.
- Compliance with privacy regulations: It can help organizations comply with privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
- Improved operational efficiency: privacy by design can help organizations to improve their operational efficiency by reducing the need to manage privacy compliance issues on an ad hoc basis.
- Improved customer experience: Through the framework, organizations can provide a better customer experience by giving users more control over their personal data.
- It can help organizations to improve their reputation: Organizations that are seen as being committed to protecting privacy are more likely to be trusted by their customers and partners.
- It can help organizations attract and retain top talent: In today’s world, employees are increasingly concerned about their privacy. Organizations that adopt the extraordinary privacy framework are more likely to attract and retain top talent who value privacy.
- Enhanced innovation: Organizations that are compliant with privacy by design can innovate more freely, without having to worry about violating privacy laws.
- It can help to prevent fraud and cybercrime: By building privacy into technology from the outset, organizations can make it more difficult for criminals to steal personal data.
- It can help to protect individuals’ rights: It gives individuals more control over their personal data, which can help to protect their privacy and security.
Steps for Privacy by Design Implementation:
There are a number of steps that organizations can take for the implementation of privacy framework, including:
- Appointment of a Data Protection Officer (DPO): A DPO is a person who is responsible for overseeing the data protection strategy and implementation of an organization. They can help to ensure that an organization is following the best practices of data protection and privacy, and can also act as a point of contact for data subjects, regulators, and other stakeholders.
- Writing a Privacy Policy: A Privacy Policy is a document that informs users about how their personal information is collected, used, shared, and protected by an organization. It can help an organization communicate its data protection practices and policies to its users, and also help the company comply with the legal requirements of transparency and accountability. A Privacy Policy should be clear, concise, accurate, and accessible to the respective users of the organization.
- Monitor and audit: Organizations should monitor their information systems and technologies for privacy breaches. They should also conduct regular audits to ensure that Privacy by design principles are being implemented effectively.
- Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA): A DPIA is a process that helps identify and minimize the data protection risks of a project. It can help an organization assess whether it needs to process personal information, how it will protect it, and how it will comply with data protection laws and principles.
- Design for privacy: Organizations should design information systems and technologies with privacy in mind. This means collecting the minimum amount of personal data necessary, using encryption and other security measures to protect data, and giving users control over their personal data.
- Educate employees: Employees should be trained on the organization’s privacy policies and procedures. They should also be aware of the privacy risks associated with their work and how to mitigate those risks.
- Involve stakeholders: Organizations should involve stakeholders, such as customers, employees, and privacy experts, in the development and implementation of Privacy by Design. This will help to ensure that the organization’s privacy practices are aligned with the needs of its stakeholders.
- Use privacy-enhancing technologies: Organizations can use privacy-enhancing technologies, such as encryption, pseudonymization, and anonymization, to protect personal data. These technologies can help to reduce the risk of privacy breaches and to make it more difficult for unauthorized individuals to access personal data.
- Bring transparency: Organizations should be transparent about their data collection, use, and disclosure practices. This means providing users with clear and concise information about how their personal data is being used. It also means giving users the ability to access their personal data and to challenge the accuracy of the data.
- Bring accountability: Organizations should be accountable for their privacy practices. This means having a process for handling complaints and for responding to privacy breaches. It also means having a process for reporting on the organization’s privacy practices.
Shortcomings of Privacy by Design:
- It can be difficult to implement since it requires a significant investment of time and resources to implement effectively. This can be a challenge for organizations that are not well-resourced or that do not have a strong commitment to privacy.
- Staying up-to-date with the latest advancements in technology can be quite challenging. Cause it is a dynamic framework that needs to be updated regularly to keep up with the changing landscape of technology. This can be a challenge for organizations that do not have the resources or expertise to stay up-to-date on the latest privacy trends.
- It can be difficult to measure the effectiveness of Privacy by design. There is no single metric that can be used to measure the effectiveness of the framework. This can make it difficult for organizations to assess whether or not they are implementing it effectively.
- It can be difficult to get buy-in from all stakeholders. Because it requires the cooperation of all stakeholders, including employees, customers, and partners. This can be a challenge, especially if there is not a strong commitment to privacy across all stakeholders.